Business Analyst
A Business Analyst analyzes business processes, identifies opportunities for improvement, and translates requirements into actionable solutions to achieve organizational goals.
Description
A Business Analyst examines business processes, identifies areas for optimization, and collaborates with stakeholders to gather and document requirements, enabling the development of effective solutions that align with organizational goals and drive operational improvements. They bridge the gap between business needs and technology by facilitating communication and ensuring projects meet user expectations.
Qualification
Business Analysts typically qualify for their positions through a combination of education, skills, and experience. Many Business Analysts graduated in Business Administration, Business Computing, Information Technology, Economics, or a related discipline. However, some companies do not require a certain academic background in order to qualify for this role.
Skills
Business Analyst salary
Junior Business Analyst
46.000 – 57.000€
Senior Business Analyst
60.000 – 76.000€
Lead Business Analyst
75.000 – 96.000€

Tasks of a Business Analyst
- Requirements Management: Organize, prioritize, and manage requirements to guide project development and implementation.
- Communication: Facilitate and align different teams, departments, and stakeholders.
- Data Analysis: Examine data to uncover insights, trends, and patterns that inform decision-making.
- Feasibility Analysis: Assess the feasibility of proposed solutions in terms of technical, financial, and operational aspects.
- Process Optimization: Analyze processes, implement changes and monitor metrics post-implementation to refine processes and solutions.
- Change Management: Support the implementation of new processes or systems by assisting with training and addressing user concerns.
- Project Management: Manage and coordinate available resources to realize projects.
Business Analyst Tools
- Data Analysis: Excel, Python or R to conduct advanced data analysis and statistical modeling.
- Project Management: Track tasks, user stories, and project progress with Jira, Trello or Asana.
- Docs: Create and collaborate on docs with Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
- Documentation: Managing and sharing docs with SharePoint, Confluence or Notion.
- Communication: Seamless communication tools like Microsoft Teams or Slack.
- Mockups: Creating mockups and prototypes of user interfaces with Sketch, Figma, or Balsamiq.
- Process Modeling: Creating flowcharts, process diagrams, and visual representations with Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart or Miro.
- Visualization: Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets for basic visualizations, Tableau or Power BI for advanced and interactive data visualizations.
- Web Conferencing: Catching up with stakeholders through Zoom, WebEx, Teams or Google Meet.
Business Analysts types
There are different specializations of Business Analysts like:
- Finance Business Analyst
- IT Business Analyst
- Process Business Analyst
- Data Analyst
Business Analyst career development
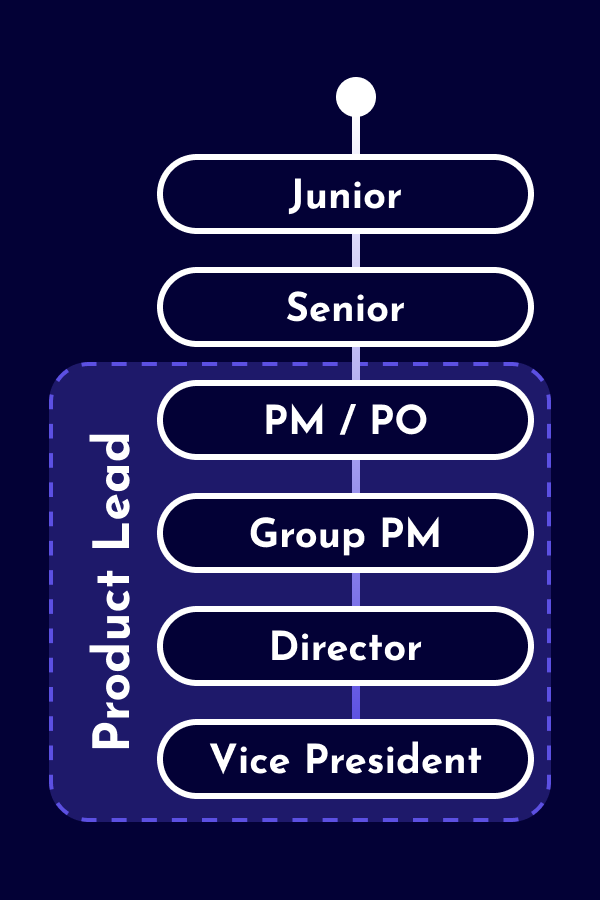
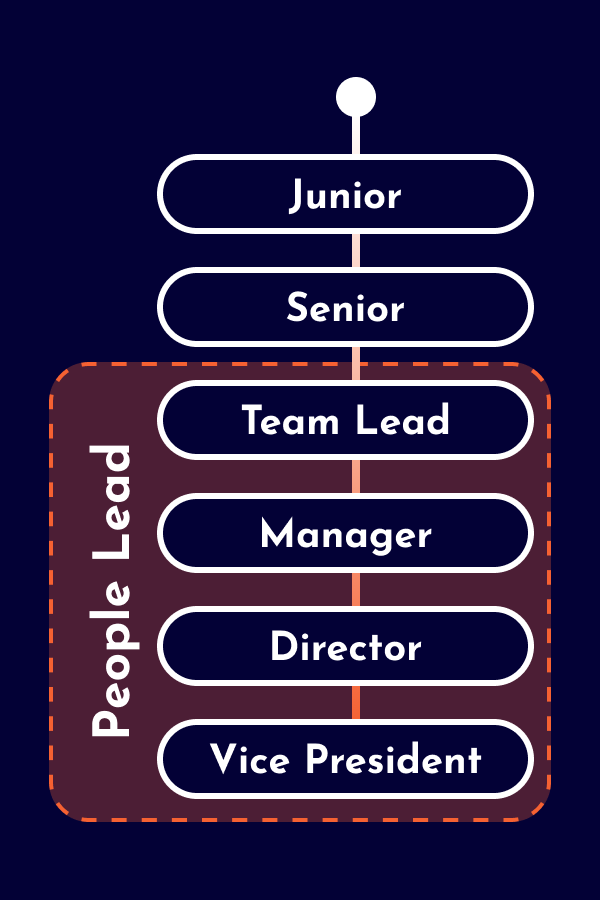
The career as a Business Analyst starts as an individual contributor (IC) with business understanding and domain knowledge, but without people responsibility. Depending on the company, distinctions are made between junior and senior levels. Some Business Analysts opt for leadership positions as People Leads (e.g. Team Lead, Engineering Manager, Chapter Lead) or Product Leads (e.g. Product Manager, Product Owner). Additionally, there are also hybrid leadership roles with responsibilities across various domains.
Boost your career
No idea how to progress in your tech career? In this exclusive 1:1 coaching you'll be guided to your next best career step. Find out about your strengths, ambitions and options, and develop your individual roadmap.
Related data roles
> Boost your tech career
Receive valuable insights about career development and leadership in tech. Right to your inbox!