Data Scientist
Data Scientists analyze and interpret complex data to extract valuable insights, develop predictive models, and drive informed decision-making within organizations.
Description
Data Scientists utilize advanced statistical, machine learning, and data analysis techniques to explore and interpret large datasets, identifying trends, patterns, and actionable insights. They design and build predictive models and algorithms that enable forecasting, classification, and recommendation systems. Data Scientists also collaborate with cross-functional teams to translate their findings into business strategies, improving processes and outcomes. Data Scientist are required in all industries, starting from medium-sized companies to large corporates.
Qualification
Data Scientists typically qualify through a combination of academic education, skills, and experience. Many Data Scientists graduated in Mathematics, Computer Science, Economics or Physics. However, there is an increasing number of individuals transitioning to Data Science without (this particular) educational background. The role Data Scientist is around for approximately 15 years.
Fähigkeiten
Data Scientist salary
Junior Data Scientist
48.000 – 58.000€
Senior Data Scientist
68.000 – 81.000€
Lead Data Scientist
83.000 – 107.000€

Tasks of a Data Scientist
- Collect and preprocess large and complex datasets from various sources.
- Clean, transform, and organize unstructured data to prepare data analysis.
- Perform exploratory data analysis to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- Select, create, and refine relevant variables for model input (feature engineering).
- Develop statistical models to explain relationships within the data and validate hypotheses.
- Create and apply machine learning algorithms for predictive and prescriptive analytics.
- Build classification, regression, clustering, and recommendation models as needed.
- Collaborate with domain experts and business stakeholders to understand objectives.
- Communicate results and present findings to non-technical stakeholders.
Data Science Use Cases
- Customer Segmentation: Identification and division of customer groups.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Improving logistics and production efficiency and costs.
- Fraud Detection: Identification of fraud attempts (e.g., in payment services).
- Personalization: Calculation of personalized content for social media and shopping.
- Predictive Maintenance: Determining maintenance schedules based on sensor data.
- Price Optimization: Determining optimal prices to increase revenue.
- Risk Analysis: Determining probabilities and risks (e.g., in insurance).
Industries
Data Scientist Tools
- Programming Languages: Python, R ad Julia for data analysis, machine learning, statistical analysis, data visualization, and research.
- Integrated Development Environments: Interactive environment to compose code like Visual Studio Code, Jupyter Notebook, PyCharm, and RStudio.
- Data Manipulation and Analysis: Pandas for data analysis and manipulation. NumPy for numerical computations and array manipulation.
- Big Data Tools: Apache Spark (Python, Scala) to process large-scale datasets in distributed computing environments.
- Cloud Platforms: Hyperscaler like AWS, Google Cloud and Azure which provide scalable infrastructure to for data transformation and model deployment.
- Machine Learning Libraries: Popular Python libraries like Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Keras, XGBoost and LightGBM.
- Collaboration and Communication Tools: JupyterHub: For collaborative Jupyter Notebook environments.
- Data Visualization: Matplotlib, Seaborn forPython and ggplot2 for R.
Data Scientist career development
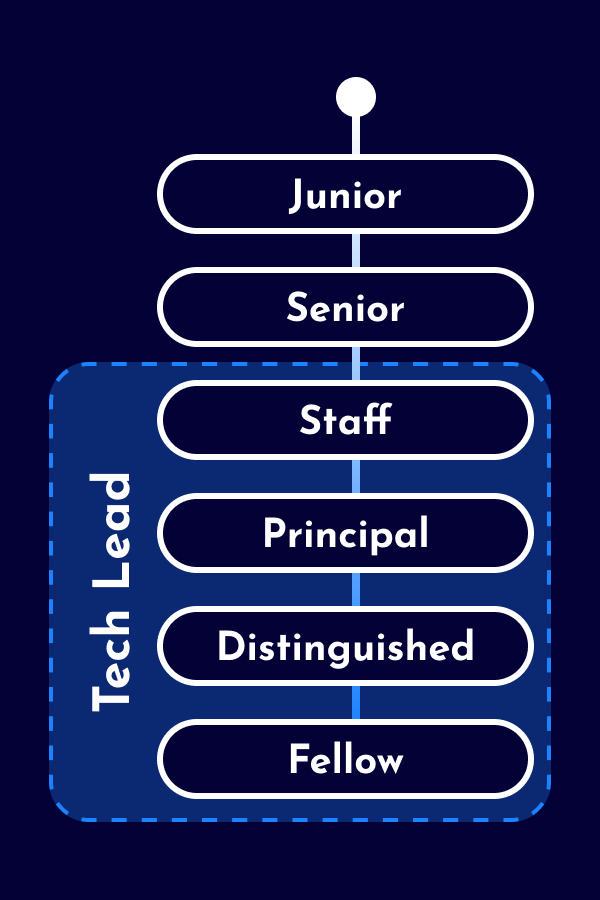
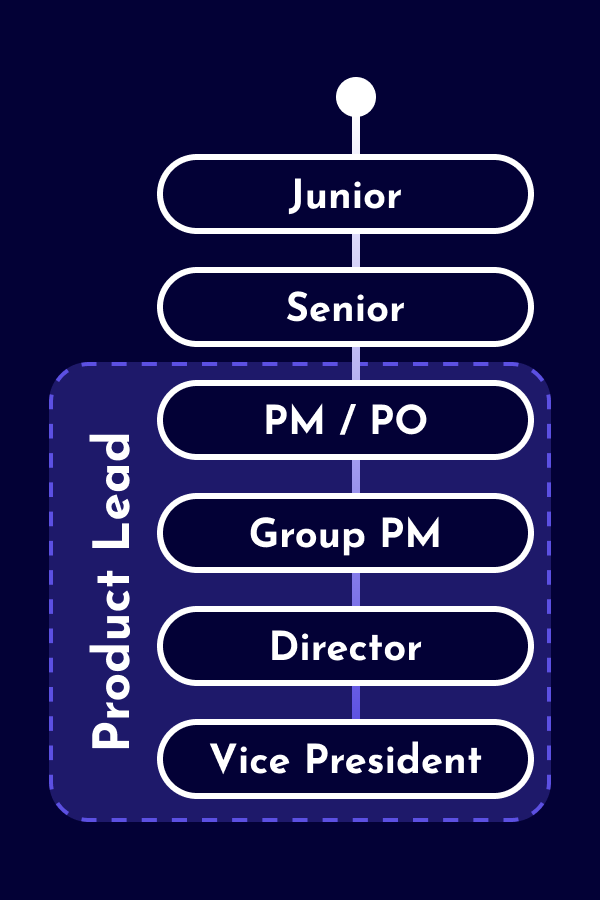
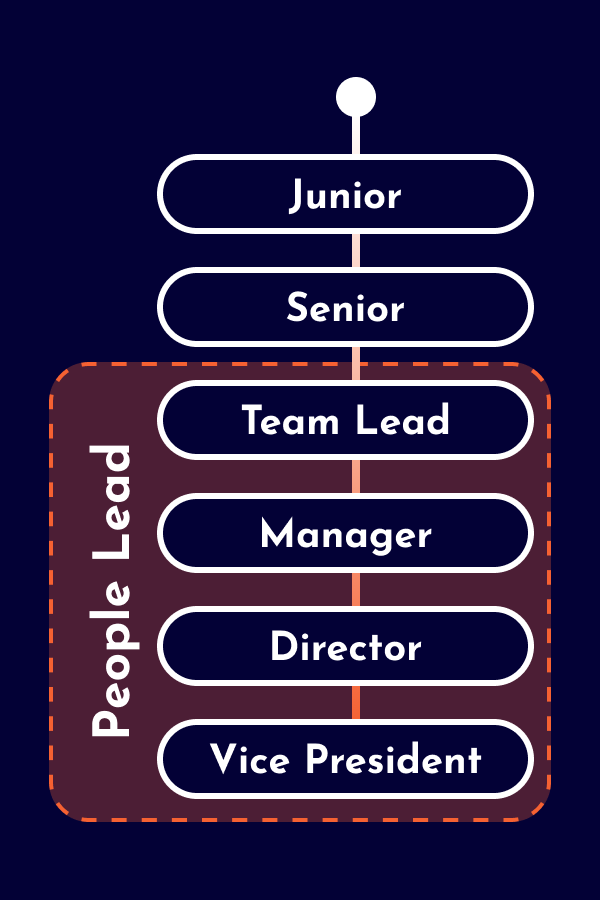
The career as a Data Scientist starts as an individual contributor with technical expertise and domain knowledge, but without people responsibility. Depending on the company, distinctions are made between junior and senior levels. Larger companies offer technical leadership positions for Data Scientist (e.g., Staff Data Scientist and Principal Data Scientist). As alternative to technical leadership roles, some Data Scientist opt for leadership positions as People Leads (e.g. Team Lead, Engineering Manager, Chapter Lead) or Product Leads (e.g. Product Manager, Product Owner). Additionally, there are also hybrid leadership roles with responsibilities across various domains.
Boost your career
No idea how to progress in your tech career? In this exclusive 1:1 coaching you'll be guided to your next best career step. Find out about your strengths, ambitions and options, and develop your individual roadmap.
Related data roles
> Boost your tech career
Receive valuable insights about career development and leadership in tech. Right to your inbox!