Data Analyst
Data Analysts analyze and interpret data to extract insights, identify trends, and support data-driven decision-making within organizations.
Description
Data Analysts collect, clean, and organize data from various sources, then use statistical and analytical techniques to uncover patterns, trends, and insights within the data. They create visualizations and reports to communicate findings to stakeholders, assisting businesses in making informed decisions and optimizing processes based on data-driven insights. Data Analysts are required in companies of all sizes and industries.
Qualification
Data Analysts typically qualify for their positions through a combination of education, skills, and experience. Many Data Analysts hold a bachelor's or master's degree in Statistics, Mathematics, Computer Science, Economics or Engineering. Due to high demand, an increasing number of individuals are transitioning to roles such as Data Analyst and other data-related positions through bootcamps.
Skills
Data Analyst salary
Junior Data Analyst
43.000 – 56.000€
Senior Data Analyst
60.000 – 76.000€
Lead Data Analyst
71.000 – 91.000€

Tasks of a Data Analyst
- Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources, including databases, spreadsheets, APIs, and more.
- Data Cleaning: Preprocessing and cleansing data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Data Transformation: Applying transformations such as normalization, aggregation, and feature engineering.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Examining data to discover patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- Statistical Analysis: Using statistical methods to derive insights and make data-driven decisions.
- Hypothesis Testing: Conducting tests to validate assumptions and draw conclusions.
- Data Visualization: Creating graphs, charts, and interactive dashboards to visually represent findings.
- Reporting: Presenting analysis results in clear and understandable reports for stakeholders.
-
Communication: Explaining complex findings to non-technical audiences and stakeholders.
Data Analyst Tools
- Spreadsheet Software: Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets for basic data analysis and manipulation.
- Query Languages: SQL and alike for querying and manipulating data from databases.
- Data Analysis Languages: Python or R for data analysis, manipulation, and statistical modeling.
- Specialized Statistical Tools: R for advanced statistical analysis and modeling. SPSS or SAS for specialized statistical analysis.
- Data Visualization Tools: Tableau, Power BI, or similar tools for creating visualizations and interactive dashboards.
-
Text Editors and IDEs: Visual Studio Code, PyCharm, or RStudio to compose code.
-
Office Suites: Microsoft Office or Google Workspace for creating reports and presentations.
Data Analyst Use Cases
- How did sales perform in the last quarter compared to the previous year?
- What was the turnover rate in sales over the last 4 weeks?
- What is the reason for the significant increase in conversion rates?
- What is the cost incurred for acquiring a lead?
- Which marketing campaign has brought the most new customers to the company?
Data Analyst career development
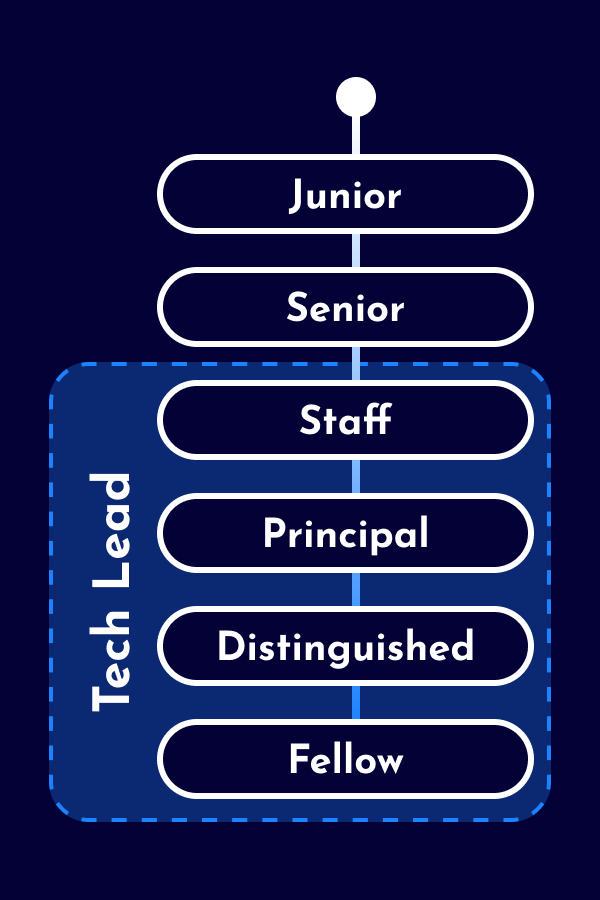
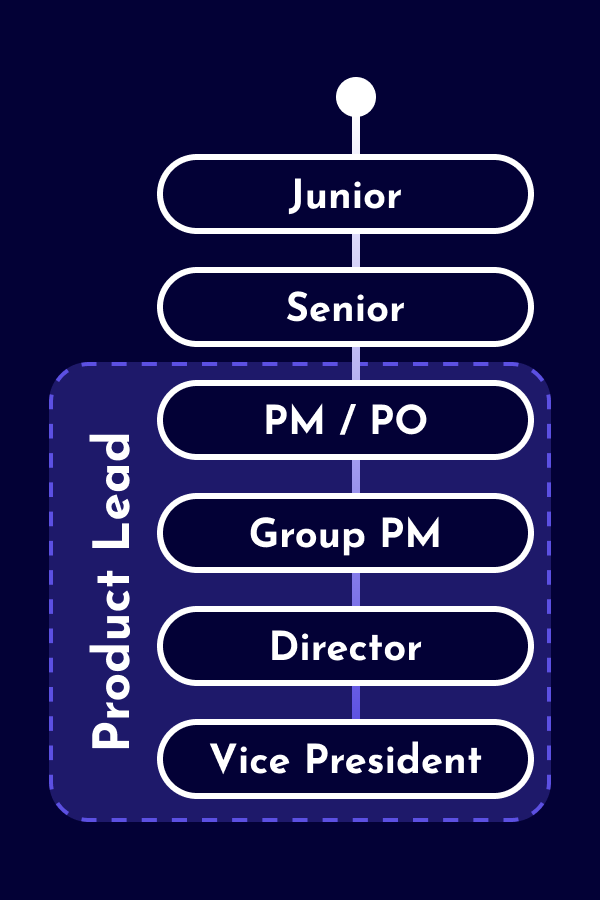
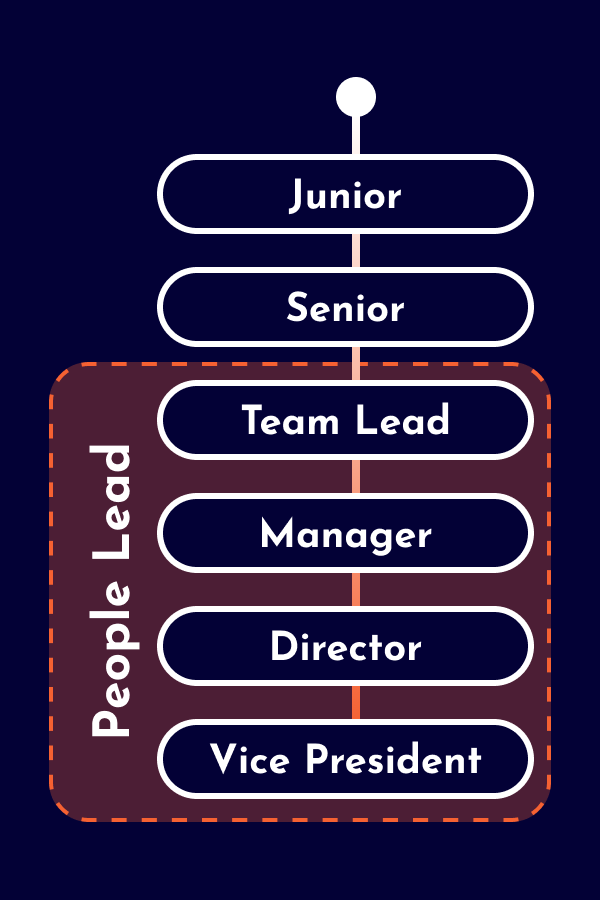
The career as a Data Analyst starts as an individual contributor with technical expertise and domain knowledge, but without people responsibility. Depending on the company, distinctions are made between junior and senior levels. Larger companies offer technical leadership positions for Data Analysts (e.g., Staff Data Analyst and Principal Data Analyst). As alternative to technical leadership roles, some Data Analysts opt for leadership positions as People Leads (e.g. Team Lead, Engineering Manager, Chapter Lead) or Product Leads (e.g. Product Manager, Product Owner). Additionally, there are also hybrid leadership roles with responsibilities across various domains.
Boost Your Career
No idea how to progress in your tech career? In this exclusive 1:1 coaching we guide you to your next career step. Find out about your strengths, define your career options and build a roadmap. Discuss your options with a competent partner with years of experience in IT and reach your next career level faster.
Related data roles
> Boost your tech career
Receive valuable insights about career development and leadership in tech. Right to your inbox!